Tuesday, April 2, 2024
How to Recognize and Avoid Phishing Attacks: A Complete Guide
Posted by
Cybersecurity Expert
@cybersecurity-expert
InfoSec Analyst
@infosec-analyst

Introduction: The Growing Threat of Phishing Attacks
In today's digital age, phishing attacks have become increasingly sophisticated and prevalent. According to the FBI's Internet Crime Report, phishing was the most common type of cybercrime in 2023, with over 300,000 reported incidents resulting in losses exceeding $52 million. These deceptive tactics aim to steal sensitive information such as login credentials, financial details, and personal data by masquerading as legitimate entities.
This comprehensive guide will help you:
- Identify common phishing techniques
- Recognize warning signs
- Implement effective strategies to safeguard yourself against these costly cyber threats
- Understand how PCI DSS compliance requirements address phishing risks
What Is Phishing?
Phishing is a type of social engineering attack where cybercriminals attempt to trick individuals into revealing sensitive information by impersonating trusted entities. The term "phishing" reflects the concept of "fishing" for information using bait—in this case, deceptive communications designed to appear legitimate.
These attacks typically arrive via:
- Text messages
- Phone calls
- Social media platforms
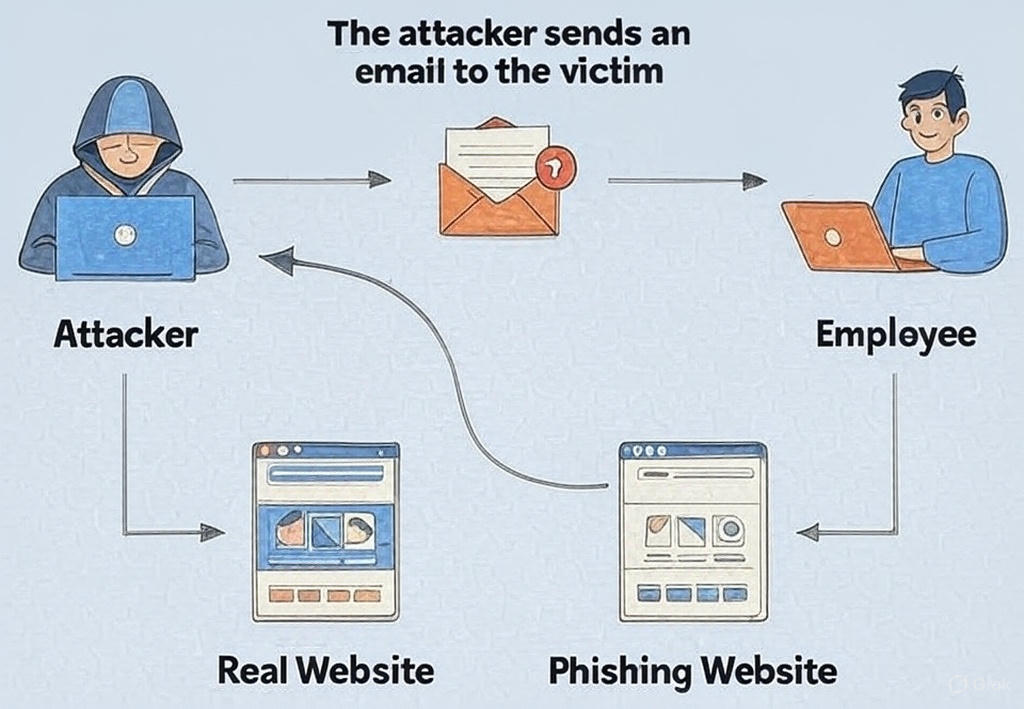
The goal is to manipulate recipients into actions that compromise their security, such as:
- Clicking malicious links
- Downloading infected attachments
- Providing confidential information
The financial impact of successful phishing attacks can be devastating:
- For individuals: Identity theft, drained bank accounts, and damaged credit scores
- For businesses: The average cost of a data breach from phishing reached $4.24 million in 2023 (IBM's Cost of a Data Breach Report)
Common Phishing Techniques
Cybercriminals employ various methods to execute phishing attacks. Familiarizing yourself with these techniques can help you identify and avoid them:
| Technique | Description |
|---|---|
| Email Phishing | The most common form, where attackers send emails appearing to be from legitimate organizations |
| Spear Phishing | Targeted attacks directed at specific individuals or organizations, often with personalized information |
| Smishing | Phishing conducted via SMS text messages |
| Vishing | Voice phishing using phone calls to deceive victims |
| Clone Phishing | Duplicating legitimate communications but replacing original links with malicious ones |
| Whaling | Attacks targeting high-profile individuals like executives or public figures |
How to Recognize Phishing Attempts
Being able to identify warning signs is your first line of defense. Here are key indicators of a phishing attempt:
- Suspicious Sender Details: Examine the sender's email address for subtle differences or misspellings (e.g., "support@amaz0n.com" vs. "support@amazon.com").
- Urgent or Threatening Language: Messages like "Your account will be suspended in 24 hours" or "Immediate action required" aim to pressure you into acting quickly.
- Poor Grammar and Spelling: Legitimate companies typically avoid spelling mistakes or awkward phrasing—errors suggest a phishing attempt.
- Suspicious Links and Attachments: Hover over links (don't click) to check the URL; avoid unexpected attachments with extensions like .exe, .zip, or .scr.
- Requests for Sensitive Information: Legitimate organizations rarely ask for passwords or credit card details via email or text.
- Unusual or Generic Greetings: Look out for generic salutations like "Dear Customer" instead of your name.
{/* SVG Placeholder: Legitimate vs. Phishing Email - Side-by-side comparison of legitimate and fraudulent emails. Left side shows a legitimate email with green checkmarks highlighting security features. Right side shows a phishing email with red X marks pointing out suspicious elements. /}
{/ SVG Placeholder: Spoofed Email Address - Close-up comparison of legitimate email address (support@amazon.com) vs. spoofed address (support@amaz0n.com) with zero instead of 'o', highlighting the subtle character replacement. */}
Psychological Tactics Used in Phishing
Phishers exploit psychological principles to manipulate targets. Understanding these tactics can help you resist them:
| Tactic | How It Works | Examples | Psychological Effect |
|---|---|---|---|
| Urgency | Creates time pressure for quick decisions | "Act now or lose access to your account" | Triggers fear of loss, bypassing rational thought |
| Authority | Impersonates trusted figures for credibility | "Message from your CEO" | Exploits tendency to obey authority |
| Social Proof | Suggests others have complied | "Join 10,000+ customers who verified" | Leverages inclination to follow the crowd |
By recognizing these triggers, you can pause and evaluate messages critically.
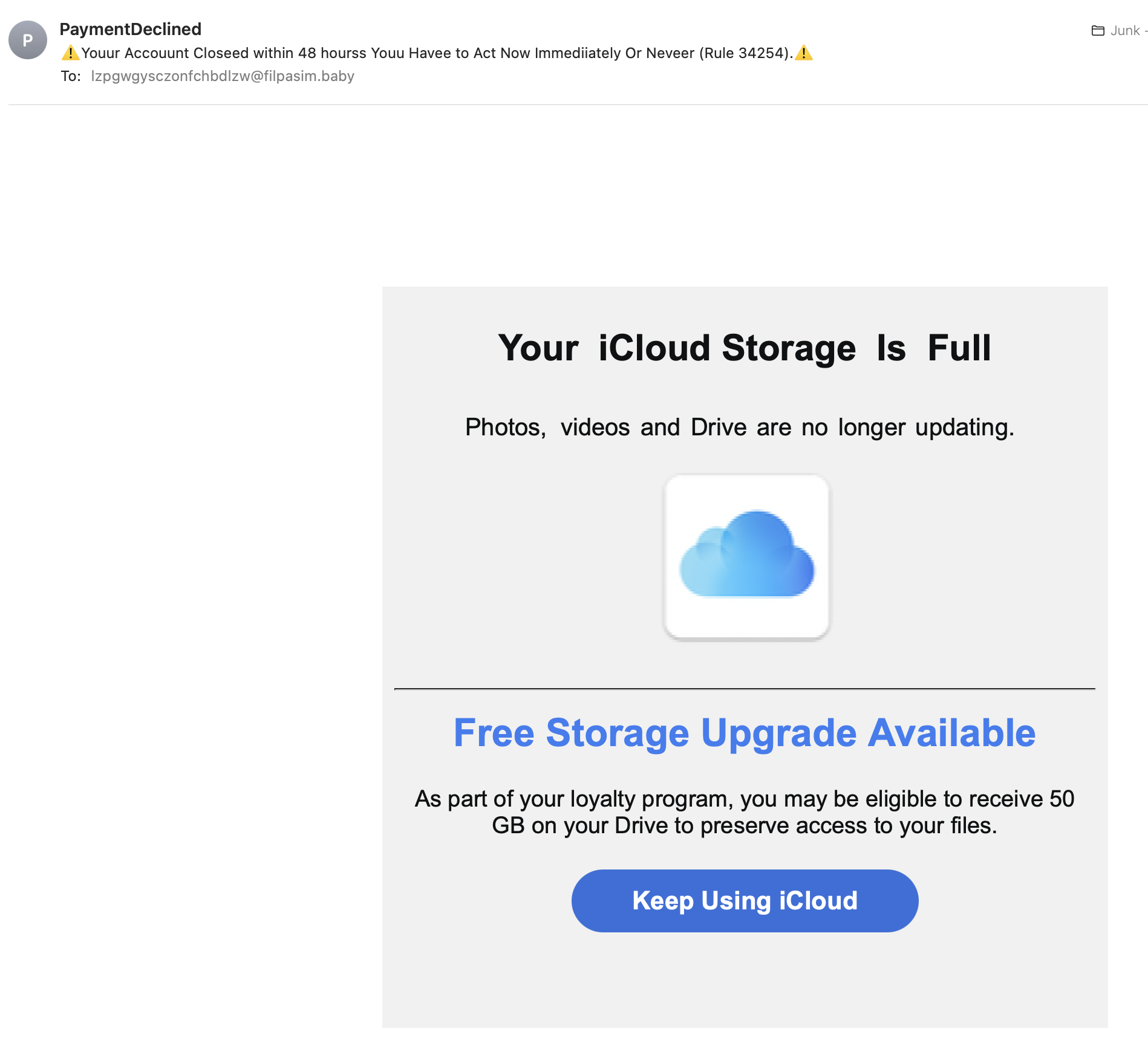
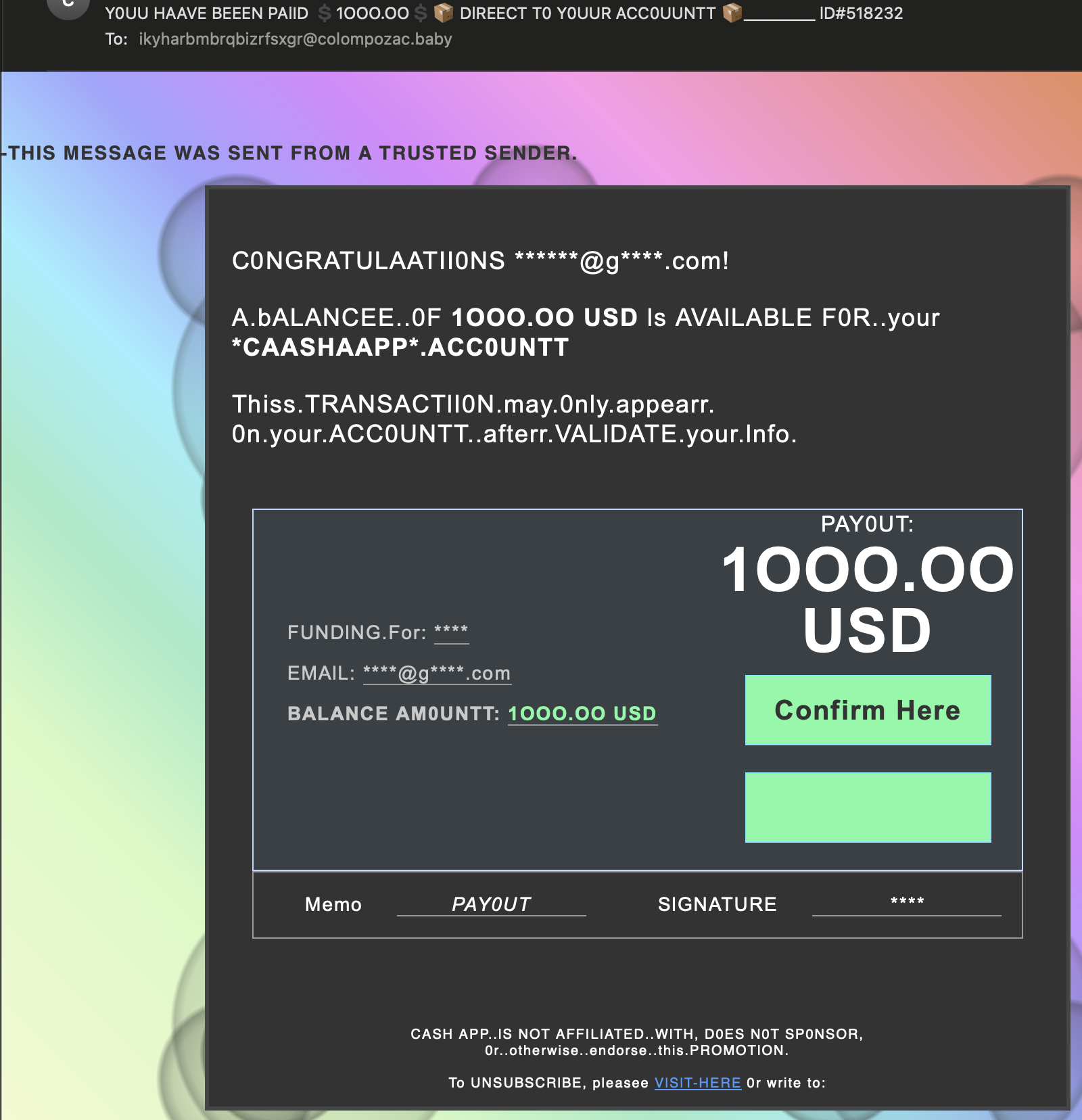
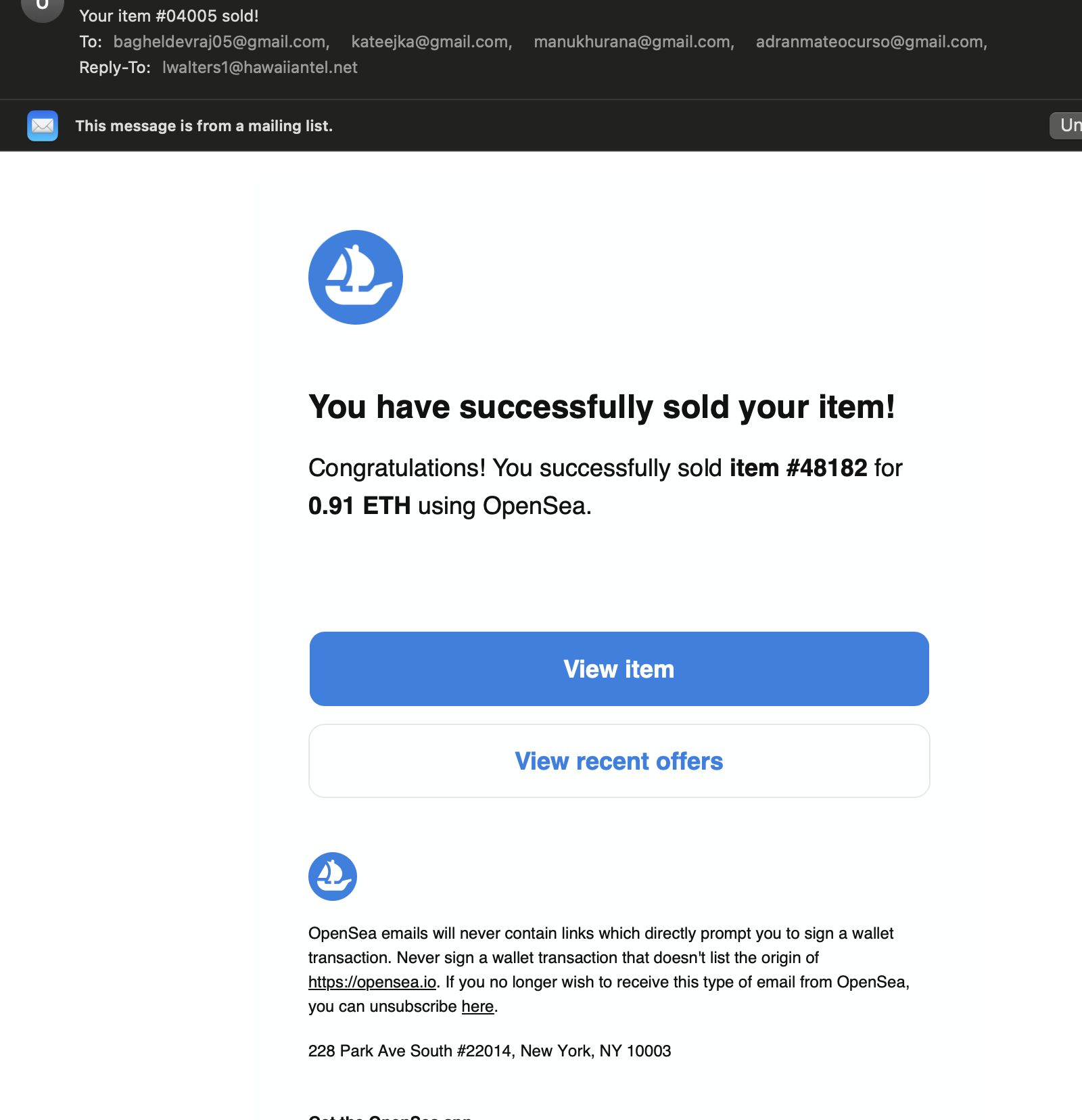
Real-World Phishing Examples
Understanding phishing in practice can sharpen your detection skills:
Emerging Phishing Trends
As technology evolves, phishing tactics adapt. Stay aware of these trends:
- AI-Generated Phishing: AI crafts convincing messages with fewer errors and personalized content.
- QR Code Phishing (Quishing): Malicious QR codes lead to fake websites when scanned.
- Business Email Compromise (BEC): Targets businesses for fraudulent wire transfers, often impersonating executives.
- Hybrid Phishing: Combines channels (e.g., email + phone) for greater legitimacy.
Effective Strategies to Avoid Phishing Attacks
Prevent phishing with these key practices:
| Strategy | Description |
|---|---|
| Verify the Sender | Use official contact details to confirm legitimacy, not those in the message |
| Use Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) | Adds an extra security layer beyond passwords |
| Keep Software Updated | Install updates to patch vulnerabilities phishers might exploit |
| Use a Password Manager | Maintains strong, unique passwords and identifies fake sites |
| Think Before Clicking | Assess messages for oddities before acting |
| Use Email Security Tools | Enable filters to catch phishing attempts |
PCI DSS Controls Addressing Phishing Risks
Organizations that process payment card data must comply with the Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS). The standard includes several requirements specifically designed to address phishing threats:
| Requirement | Focus Area | Relevance to Phishing |
|---|---|---|
| 12.6.3 | Security Awareness Training | ✅ Directly requires phishing awareness |
| 5.4.1 | Anti-Phishing Mechanisms | ✅ Explicitly mandates phishing protection |
| 8.x | Authentication & Access | ✅ Helps limit phishing impact (e.g., MFA) |
| 12.10 | Incident Response | ✅ Ensures proper response to successful attacks |
| 6.3 | Secure Development | ✅ Prevents vulnerabilities exploitable by phishing |
| 4.x | Data Encryption | ✅ Reduces impact of compromised credentials |
Key PCI DSS Requirements for Phishing Protection
Requirement 12.6.3 mandates that all personnel receive security awareness training upon hire and at least annually, with specific focus on phishing and social engineering attacks.
Requirement 5.4.1 explicitly requires organizations to implement processes and automated mechanisms to detect and protect personnel against phishing attacks.
Requirements in section 8.x establish strong authentication controls that limit the damage from compromised credentials:
- 8.3.6: Requires MFA for all non-console administrative access
- 8.3.7: Requires MFA for all remote network access to the cardholder data environment
- 8.2.8: Mandates strong password policies
Requirement 12.10 ensures organizations have a documented incident response plan that can be activated if a phishing attack succeeds, minimizing the damage.
Requirement 6.3 focuses on secure software development practices that reduce the likelihood of vulnerabilities that phishing attacks might exploit.
Requirements in section 4.x ensure sensitive data remains encrypted even if access credentials are compromised through phishing.
Implementing these PCI DSS controls not only helps achieve compliance but also significantly reduces an organization's vulnerability to phishing attacks and their potential impact.
What to Do If You've Been Phished
If you suspect a phishing breach, act quickly:
- Change passwords for affected accounts
- Contact financial institutions if banking details were exposed
- Monitor accounts for unusual activity
- Report the phishing to the impersonated organization
- File a report with law enforcement and the FBI's IC3
- Place a fraud alert on your credit reports
Employee Training for Organizations
Businesses should adopt a comprehensive approach that aligns with PCI DSS requirements:
- Conduct regular security awareness training (required by PCI DSS 12.6.3)
- Run simulated phishing exercises to test effectiveness
- Establish clear reporting procedures for suspected phishing
- Foster a security-first culture across the organization
- Update employees on new phishing trends and techniques
- Document training activities to demonstrate PCI DSS compliance
Conclusion
Phishing attacks continue to grow more sophisticated, but vigilance combined with the strategies in this guide can significantly reduce your risk. Organizations should implement a multi-layered approach that includes both technical safeguards and comprehensive awareness training.
For businesses that handle payment card data, following PCI DSS requirements provides a structured framework to address phishing risks effectively. Requirement 5.4.1 specifically mandates phishing protection, while other requirements like 12.6.3 (security awareness) and 8.x (strong authentication) provide additional layers of defense.
Organizations that process payment card data should be aware of upcoming regulatory changes. The Payment Card Industry Security Standards Council (PCI SSC) has announced that by March 31, 2025, anti-phishing mechanisms will become mandatory for PCI DSS compliance under the new v4.0.1 framework.
Requirement 5.4.1 specifically mandates "processes and automated mechanisms to detect and protect personnel against phishing attacks," with security awareness training alone no longer being sufficient. Businesses will need to implement email authentication protocols such as SPF, DKIM, and DMARC.
Take a moment to verify communications before taking action—it could prevent devastating consequences. Stay informed, cautious, and secure online.
For more, explore our articles on Password Security, Internet Safety Basics, PCI DSS Compliance, and PCI DSS v4.0.1: New Anti-Phishing Requirements Coming in 2025.
Related Posts
PCI DSS v4.0.1: New Anti-Phishing Requirements Coming in 2025
Learn about the upcoming PCI DSS v4.0.1 compliance mandate requiring anti-phishing mechanisms by March 2025, what it means for your business, and how to prepare with SPF, DKIM, and DMARC implementation.
12 Essential PCI DSS Practices to Protect Your Card Data
Learn the 12 critical PCI DSS compliance practices that every business handling payment card data must implement to secure their payment environment, prevent data breaches, and maintain customer trust.
Using Network Segmentation to Reduce PCI DSS Scope
Learn how to effectively implement network segmentation to minimize your PCI DSS compliance scope, reduce risk, and protect cardholder data environments while optimizing security resources and costs.